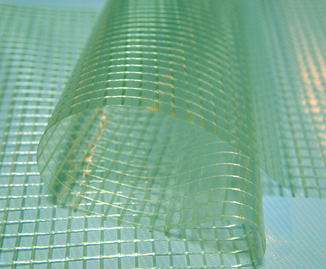
The core of the long-term protection ability of PE PVC stripes tarpaulin roll fabric material lies in the exquisite combination of two polymer materials, polyethylene (PE) and polyvinyl chloride (PVC). The synergistic effect of PE and PVC stems from the molecular structure characteristics of the two that are completely different but highly complementary. The polyethylene molecular chain is mainly arranged linearly, and the carbon-carbon single bond gives it good flexibility and low-temperature adaptability. It can still maintain elasticity at extremely low temperatures of -40°C, effectively avoiding the brittle cracking of the material. Its non-polar molecular structure has a natural barrier ability to ultraviolet rays and can delay the process of photoaging. Polyvinyl chloride, with the introduction of chlorine atoms, forms a highly cross-linked rigid molecular chain, which not only significantly improves the hardness and wear resistance of the material, but also gives it acid and alkali resistance and anti-fungal properties due to the chemical stability of the chlorine element. When the two materials are fused through a special blending process, the flexible chain segments of PE are interspersed in the rigid network of PVC, forming a "rigid and flexible" interpenetrating polymer network (IPN), which not only retains the low temperature and UV resistance advantages of PE, but also strengthens the chemical protection performance of PVC, eliminating the performance shortcomings of a single material at the molecular level.
Performance upgrade driven by blending process
The compounding of materials is not a simple mixing, and the special blending process is the key to achieving a leap in performance. In the high-temperature molten state, PE and PVC undergo multiple shearing and stretching actions in the screw extruder, which promotes the full entanglement and penetration of the molecular chains. By adding a compatibilizer to reduce the interfacial tension between the two phases, PE and PVC are evenly dispersed at the nanoscale to form a continuous phase structure. This structure not only avoids the problem of material stratification or phase separation, but also creates a unique synergistic effect: when the tarpaulin is exposed to ultraviolet rays, the PE molecular chain absorbs the photon energy and quickly transfers the energy to the PVC network through intermolecular forces, avoiding local energy accumulation and degradation; in a humid environment, the dense structure of PVC prevents water molecules from penetrating, while the flexibility of PE ensures that the coating remains intact during the alternation of dry and wet, preventing water vapor from invading the base fabric. This molecular-level energy transfer and physical protection work together to enable the tarpaulin to maintain stable performance in complex environments.
Multi-level construction of weather-resistant barrier
The synergistic effect of PE and PVC is ultimately transformed into a multi-level weather-resistant protection system for tarpaulins. On the physical level, the flexibility of PE combined with the rigidity of PVC allows the tarpaulin to maintain structural integrity under the impact of strong winds and hail; on the chemical level, the chlorine atoms of PVC and the stable carbon chains of PE jointly resist acid, alkali and salt spray erosion; in terms of light aging protection, PE absorbs ultraviolet rays and PVC inhibits the generation of free radicals. The combination of the two reduces the photodegradation rate to less than 1/3 of that of a single material. This three-dimensional protection mechanism has achieved remarkable results in practical applications: whether it is cold-proof covering for polar scientific research equipment or moisture-proof protection for cargo in coastal ports, PE PVC stripes tarpaulin roll fabric material can effectively extend its service life and reduce the frequency of replacement due to environmental factors by virtue of the synergistic advantages of materials, providing users with reliable and economical protection solutions. From the interaction of molecular chains to the presentation of macroscopic performance, the collaborative innovation of PE and PVC redefines the weather resistance standards of outdoor protective materials. Through the deep integration of material science and engineering technology, PE PVC stripes tarpaulin roll fabric material transforms the characteristics of polymer materials into a solid barrier against environmental challenges, providing long-term and stable protection for outdoor application scenarios in industries such as industry, logistics, and agriculture.

 English
English CN
CN ES
ES 86-573-88890126
86-573-88890126